Field Effect Transistor is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the flow of current. FETs are three-terminal devices and their terminals are named as the source, gate and drain. FETs use either holes or electrons as charge carriers for their operation, but never both. The field-effect transistors are either fabricated with N-channel or P-channel.
FET Basics
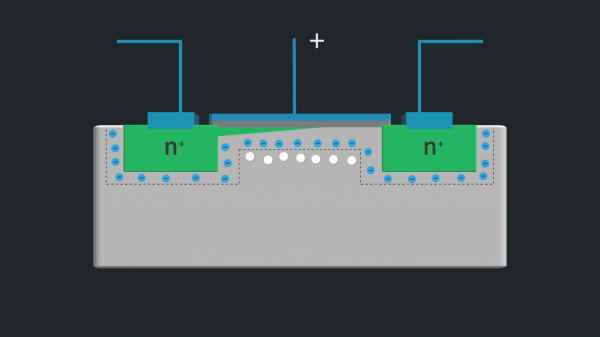
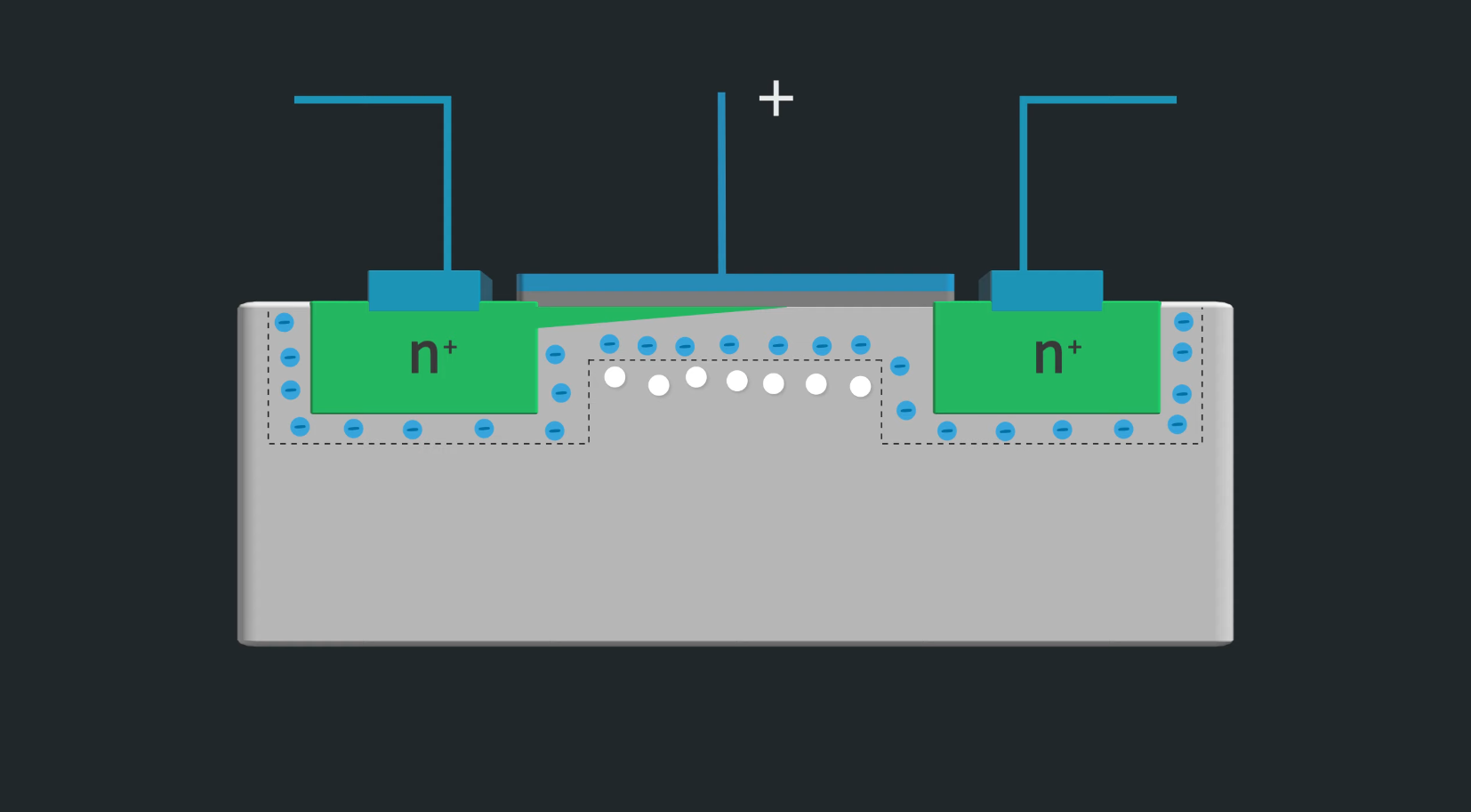
The FET is made up of a semiconductor channel with electrodes connected at either end. These electrodes are referred to as the drain and the source. A control electrode known as the gate is placed close to the channel so that its electric charge affects the channel. The gate can either enhance or deplete the number of charge carriers available in the channel when the voltage is increased. Due to this reason, there are enhancement mode FET and depletion mode FETs.
Working or Operation of FET
Let us make use of the water pipe and vessel analogy to understand how a FET works. The water source can be considered as the source of FET. The vessel that collects water can be analogous to the drain terminal of FET. Lastly, the gate terminal is analogous to the controlling tap that controls the flow of water. The way in which the controlling tap modulates the water is the same way in which the voltage at the gate terminal controls the flow of current from source to drain terminal.
Classification of FETs
The FETs are mainly classified into two types as follows:
- JFET (Junction Field-effect Transistor)
- IGFT (Insulated Gate Field-effect Transistor)
The insulated gate FET is one in which the gate is insulated by an insulation material from the semiconductor specimen. MOSFET is a popular type of IGFET that works in two modes: Depletion mode and Enhancement Mode.
In a JFET, the conduction is established by the variation of depletion width when the junction is reversed biased. There are two types of FETs according to the construction and they are classified as N channel and P channel.
Difference Between JFET and MOSFET
Some differences between JFET and MOSFET are listed in the table below:
| JFET | MOSFET |
| JFET is a three-terminal semiconductor device | MOSFET is a four-terminal semiconductor device |
| It is operated only in the depletion mode | It operates both in depletion and enhancement mode |
| It is relatively cheaper | It is expensive |
| Ideal for low noise application | Ideal for high noise application |
These were some basic information about Field effect transistors. Hope all your doubts regarding the FETs are clear.













































You must be logged in to post a comment Login